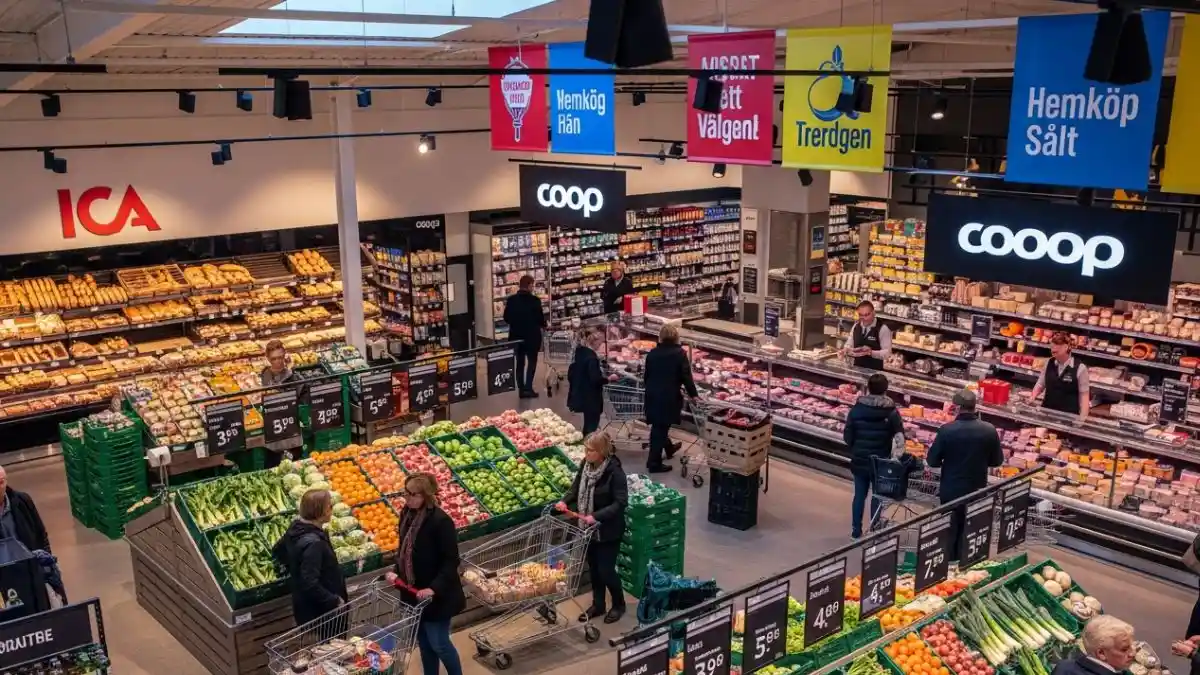
Sweden’s grocery retail market remains one of the most concentrated in Europe.
A small number of national supermarket groups control the majority of food sales, logistics flows, and supplier negotiations.
By 2026, this concentration has tightened further.
Scale, private label penetration, and distribution efficiency now determine competitive position more than store count alone.
While precise market share varies slightly by methodology, all major industry sources place the same five groups firmly at the top of Swedish grocery retail.
Below this level, remaining players are fragmented and structurally marginal.
This ranking reflects estimated national grocery market share, supported by net sales, store footprint, and workforce scale, based on publicly available FY2024–FY2025 company disclosures.
Sweden grocery market overview
Highly concentrated national structure
Strong wholesaler-backed and cooperative retail models
Among Europe’s highest private label penetration rates
Logistics and automation central to margin protection
Limited space for new national entrants
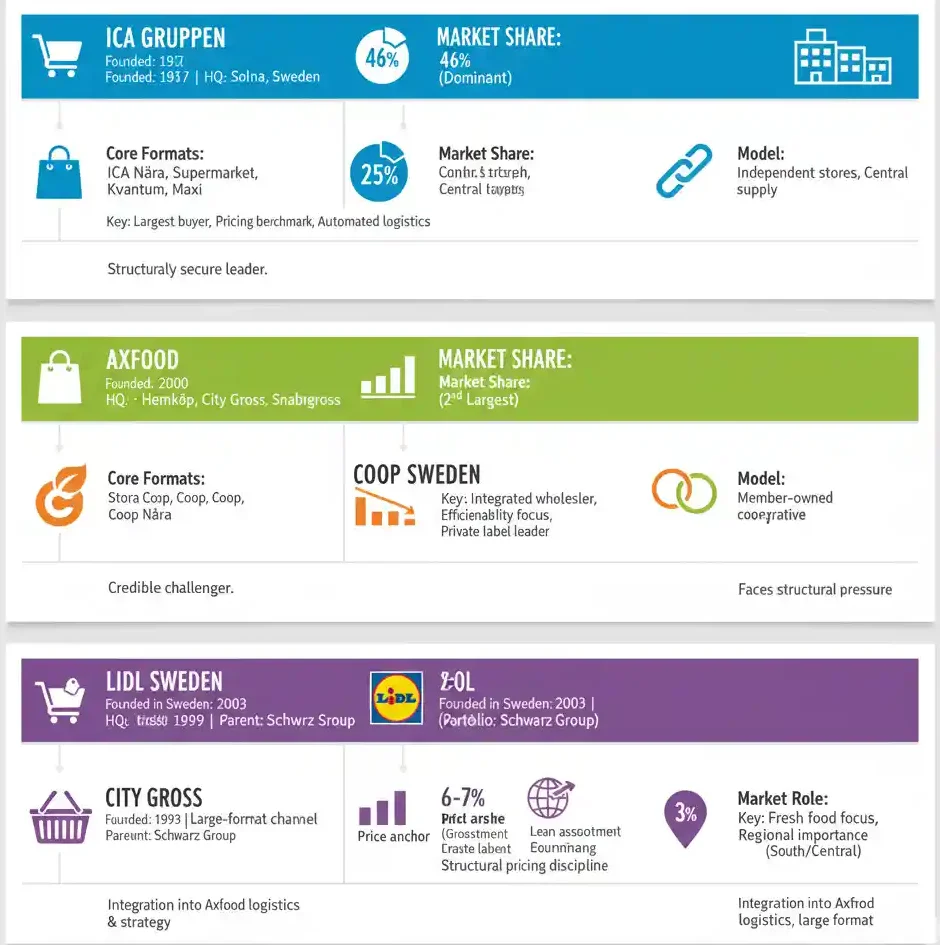
5 Supermarket Chains In Sweden By Market Share
| Rank | Supermarket group | Market share (est.) | Revenue (SEK bn) | Employees | Stores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ICA Gruppen | ~46% | 178.1 | 41,000+ | 1,260+ |
| 2 | Axfood | ~25% | 89.2 | 15,000+ | 680+ |
| 3 | Coop Sweden | ~16–17% | 58.8 | 20,000+ | 800+ |
| 4 | Lidl Sweden | ~6–7% | 22.0 | 5,300+ | 200+ |
| 5 | City Gross (Axfood) | ~3% | 3.0 | 2,800+ | 40+ |
1. ICA Gruppen
Founded: 1917
Headquarters: Solna, Sweden
Core formats
ICA Nära
ICA Supermarket
ICA Kvantum
ICA Maxi
Market position and scale
ICA remains Sweden’s dominant grocery retailer.
Its estimated market share of around 46 percent places it clearly ahead of all competitors, without breaching the symbolic 50 percent threshold often referenced in regulatory discussions.
The group’s structure is distinctive.
Stores are independently owned but centrally supplied, branded, and coordinated.
This model combines local autonomy with national purchasing power.
ICA’s store network covers urban centres, suburbs, and rural communities.
This reach gives the group unmatched leverage across fresh food, packaged groceries, and private label sourcing.
Operational relevance
Largest grocery buying organisation in Sweden
Central reference point for national pricing architecture
Critical volume partner for packaging, meat, dairy, produce, and ambient suppliers
ICA’s logistics platform is mature and highly automated.
Central category management ensures consistency, while store-level flexibility supports local range adaptation.
Private label position
Private label is embedded across all ICA tiers.
Ranges span entry price, mainstream, premium, and sustainability-led products.
This breadth supports margin stability and strong shelf control.
For suppliers, ICA often sets national standards on pack size, formulation, and compliance.
Strategic direction
Continued investment in automation and forecasting
Tightened supplier requirements
Incremental expansion of premium and sustainability ranges
ICA’s leadership position remains structurally secure.
2. Axfood
Founded: 2000
Headquarters: Stockholm, Sweden
Core formats
Willys
Hemköp
City Gross
Snabbgross
Market position and scale
Axfood is Sweden’s second-largest grocery group and the country’s strongest integrated wholesaler-retailer model.
With the full integration of City Gross completed in late 2024, Axfood’s estimated market share has risen to around 25 percent by 2026.
Unlike ICA, Axfood operates centrally controlled retail banners.
This enables faster national execution across pricing, promotions, and private label development.
Operational relevance
One of Sweden’s largest food wholesalers
Highly automated logistics and distribution network
Multi-format reach from discount to large-format retail
Axfood’s supply chain investments have focused on cost discipline and throughput efficiency.
This has supported Willys’ aggressive discount positioning while preserving profitability.
Private label leadership
Axfood is widely regarded as Sweden’s most advanced private label operator.
Key ranges include:
Garant
Eldorado
Hemköp-exclusive lines
Private label penetration is high across all formats.
This strengthens Axfood’s negotiating position with both branded suppliers and packaging partners.
Strategic direction
Private label expansion
Clearer format differentiation
Logistics efficiency over rapid store growth
Axfood remains the most credible structural challenger to ICA.
3. Coop Sweden
Founded: 1899
Headquarters: Solna, Sweden
Core formats
Stora Coop
Coop
Coop Nära
Market position and scale
Coop is Sweden’s third-largest grocery retailer, operating through a member-owned cooperative structure.
Its estimated market share of 16–17 percent reflects a gradual decline over the past decade, as discount formats have gained ground.
Coop maintains a dense national store network, particularly in urban and suburban areas.
Operational relevance
Large national footprint
Strong presence in everyday food categories
Significant sourcing volumes despite declining share
The cooperative structure provides local engagement but limits speed of execution compared with more centralised competitors.
Private label position
Coop operates several established private label ranges:
Änglamark
Coop Xtra
Coop premium selections
These ranges support Coop’s sustainability and ethics-led positioning.
Margins remain more exposed due to cost structure and price competition.
Strategic direction
Cost control and restructuring
Store profitability over expansion
Simplification of operations
Coop remains a core national player but faces ongoing structural pressure.
4. Lidl Sweden
Founded in Sweden: 2003
Parent group: Schwarz Group
Core format
Discount supermarket
Market position and scale
Lidl’s estimated market share of 6–7 percent is modest compared with other European markets, but its influence exceeds its size.
With more than 200 stores nationwide, Lidl exerts sustained downward pressure on prices across key categories.
The group reported its first sustained profitability in Sweden during FY2024–FY2025.
Operational relevance
Highly centralised European sourcing
Lean assortment strategy
Strong private label dominance
Lidl’s model limits opportunities for branded suppliers but sets efficiency benchmarks for the wider market.
Strategic direction
Lidl’s role in Sweden is structural rather than dominant.
It functions as a pricing anchor and competitive discipline mechanism.
5. City Gross
Founded: 1993
Ownership: Axfood
Market position and role
City Gross represents around 3 percent of the Swedish grocery market.
Its importance lies in format strategy rather than scale.
Following its acquisition by Axfood, City Gross has shifted from challenger status to portfolio component.
Operational relevance
Large basket sizes
Strong fresh food focus
Regional importance in southern and central Sweden
Strategic direction
Integration into Axfood logistics
Range rationalisation
Price repositioning
City Gross now serves as a complementary large-format channel within Axfood’s broader strategy.
Market structure impact
Sweden’s grocery market is defined by concentration.
The top two groups alone control more than 70 percent of national sales.
This structure shapes:
Supplier pricing power
Packaging standardisation
Speed of innovation adoption
Barriers to entry remain high due to logistics costs and real estate constraints.
Category dominance trends

Key trends shaping Swedish supermarkets:
Private label expansion across all price tiers
Fresh food as the primary traffic driver
Sustainability compliance becoming standardised
Discount pressure led by Willys and Lidl
Industry outlook
Through 2026, the Swedish grocery market is expected to remain structurally stable.
Key developments:
Increased automation in distribution
Further segmentation of private label ranges
Tighter supplier and packaging compliance standards
Limited national consolidation beyond current players
Market share shifts are likely to be incremental rather than disruptive.
Conclusion
The Swedish grocery market in 2026 is defined by scale, discipline, and private label power.
ICA remains the clear leader.
Axfood continues to strengthen its position.
Coop retains relevance under pressure.
Lidl shapes price discipline.
City Gross plays a strategic supporting role.
For suppliers, packaging groups, and logistics providers, relevance in Sweden is concentrated within these five supermarket chains.
Editor’s Note: This article is based on publicly available company financial reports, annual disclosures, and Swedish grocery market data covering FY2024–FY2025.









